Session Management Edition -- Global Dial Plan Replication(GDPR)
A Global Cisco Unified Communications Session Management Edition (Unified CM SME) which is a trunk and dial plan aggregation component for multi-site distributed call processing deployments. The Global SME is essentially a Cisco Unified Call Manager Cluster with trunk interfaces and no IP endpoints. It enables aggregation of multiple Cisco communications telephony systems, known as leaf clusters.
Centralized routing diagram
Main purpose
Server Function for CUCM will fit into one or more of the following feature sets:
Publisher Service Activation
Servers
|
Service Name
|
Activation Status
|
Publisher
This server is responsible for all of the administration updates to the other servers in the cluster. It must communicate with all other servers.
Additionally this server is used for the following functions:
Due to the administration overhead, Call control (Cisco CallManager), TFTP (Cisco TFTP) and media resource (Cisco IP Voice Media Streaming Application) functionality has been disabled, as to prevent CPU over-utilization.
Encryption services are also disabled, as this feature is not being deployed.
|
Cisco CallManager
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco Messaging Interface
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco Unified Mobile Voice Access Service
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco IP Voice Media Streaming App
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco CTIManager
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco Extension Mobility
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco Extended Functions
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco DHCP Monitor Service
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco Intercluster Lookup Service
|
Activated
|
Cisco Dialed Number Analyzer Server
|
Activated
|
Cisco Dialed Number Analyzer
|
Activated
|
Cisco TFTP
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco IP Manager Assistant
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco WebDialer Web Service
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco SOAP - CDRonDemand Service
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco CAR Web Service
|
Deactivated
|
Platform SOAP Services
|
Activated
|
Cisco AXL Web Service
|
Activated
|
Cisco UXL Web Service
|
Activated
|
Cisco Bulk Provisioning Service
|
Activated
|
Cisco TAPS Service
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco Serviceability Reporter
|
Activated
|
Cisco CallManager SNMP Service
|
Activated
|
Cisco CTL Provider Activated
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco Certificate Authority Proxy Function
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco DirSync
|
Activated
|
Subscriber Service Activation
Servers
|
Service Name
|
Activation Status
|
Subscribers
** Cisco AXL Web Service will only be enabled for Sub1 and Sub2 on each cluster
All Subscribers
Cisco CallManager service is enabled
Cisco CallManager SNMP Service is enabled
Cisco Web Dialler Web Service is enabled
Cisco Extended Functions are enabled
|
Cisco CallManager
|
Activated
|
Cisco Messaging Interface
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco IP Voice Media Streaming App
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco CTIManager
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco Extension Mobility
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco Extended Functions
|
Activated
|
Cisco DHCP Monitor Service
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco Dialed Number Analyzer Server
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco Dialed Number Analyzer
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco TFTP
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco IP Manager Assistant
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco WebDialer Web Service
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco SOAP Services
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco AXL Web Service
|
Activated**
|
Cisco UXL Web Service
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco TAPS Service
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco Serviceability Reporter
|
Deactivated
|
Cisco CallManager SNMP Service
|
Activated
|
Cisco CTL Provider
|
Deactivated
|
To ensure that the endpoints’ codec preferences are trusted as calls pass through SME, enable the SIP Profile feature “Accept Audio Codec Preferences in Received Offer” on all SIP Trunks.
Global Dial Plan Replication – GDPR and ILS
Intercluster lookup Service
(ILS)
|
The Intercluster Lookup Service (ILS) feature is used to interconnect multiple clusters together. With the ILS cluster discovery service it provides clusters to dynamically learn about remote clusters within the ILS network. ILS also supports the Global Dial Plan Replication (GDPR) feature. ILS and GDRP work together to dynamically share the global dial plan with all clusters within the ILS network.
|
Global Dial Plan Replication
(GDPR)
|
The Global Dial Plan Replication (GDPR) feature uses the ILS feature to share dial plan information between clusters within the ILS network. The information is captured by a centralized hub cluster which then propagates to all connected spoke clusters.
|
Menu: Advance Features > ILS Configurations; Select Role: For SME: ‘Hub Cluster’
Leaf clusters: ‘Spoke Cluster’
In the ‘ILS Cluster Registration’ pop up window, input in ‘Registration Server’: For SME: leave blank and click OK; For Leaf: Enter IP of Publisher node of hub cluster and click OK
Input check for ‘Exchange Global Dial Plan Replication Data with remote Clusters’
Enter route string for Cluster, which will populate, to all clusters within the ILS network. Keep default of 10 minutes for ‘Synchronize Clusters Every’ field. Route string naming convention:The route string will be a combination of Cluster ID + ‘.ils’. Example: ClusterXXX.ils
For ILS Authentication there are two options to choose from, via TLS certificates or by password. The Password would be the same entered on all clusters.
ILS network Verification
Once you have the first two networks configured, Hub and a spoke, verify connectivity at top of page. You may need to click on refresh button a few times. You can also temporary reduce ‘Synchronize Clusters Every’ to 1 minute. The screen capture below indicates there is 1 hub and 1 spoke.
View from Hub:
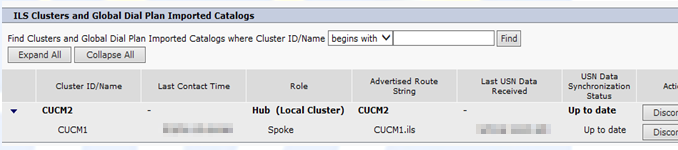
View from Spoke:
Partitions for Learned Numbers and Patterns
Configure SIP route patterns
Call Routing > SIP Route Pattern
For SME: create a SIP Pattern for each cluster it is connected to and assign the associated trunk for that clusters.
For Leafs: You only need to create one SIP Pattern in each leaf.
ILS Service Parameter configuration
Determine the required max number of learned objects.
ILS advertises locally configured enterprise alternate numbers and +E.164 alternate numbers to the ILS network where the Advertise globally via ILS option has been selected.
Click: Add Enterprise Alternate Number