Non-SSO Mobile and Remote Access through Cisco Expressway
Cisco UC mobile and remote access is a core part of the Cisco Collaboration Edge Architecture. It allows endpoints such as Cisco Jabber to have their registration, call control, provisioning, messaging and presence services provided by Cisco Unified CM when the endpoint is not within Enterprise network. The Expressway Provides secure firewall traversal and line-side support for Unified CM registrations.
This is a lab to show you step by step how it is configured. Some prerequisites you can find Cisco Expressway Deployment Guide.
Lab Devices
CUCM - 10.5.2 – 142.100.64.11
IMP – 10.5.2 – 142.100.64.15
Internal DNS – 142.100.64.20
Expressway C– 8.8 – 142.100.64.17
Expressway E– 8.8 – 142.100.64.18 (Internal IP)
Expressway E– 8.8 – 207.xx.xx.18 (External IP)
Unified CM with IMP
Server Configuration
SIP Trunk Security Profile Configuration
Trunk Configuration
Service Parameter Configuration
Domain and Internal DNS
DNS
Internal Records
The following table lists the SRV records you can provision on internal name servers so the client can discover services:| Service Record | Description |
|---|---|
| _cisco-uds | Provides the location of Cisco Unified
Communications Manager version 9 and higher. |
| _cuplogin | Provides the location of Cisco Unified Presence. |
UCM LDAP and Service Profile
LDAP Directory
UC Service Configuration
Enhanced Directory Integration (EDI)
EDI uses native Microsoft Windows APIs to retrieve contact data from the directory service.
the following are the default settings for on-premises deployments with EDI:
- Cisco Jabber integrates with Active Directory as the contact source.
- Cisco Jabber automatically discovers and connects to a Global Catalog.
the client does the following by default:
1. Gets the DNS domian from the works tation and looks up the SRV record for the Global Catalog.
2. Retrieves the address of the Global Catalog from the SRV record
Global Catalog: _gc._msdcs._tcp.domain.com
DC: _ldap._msdcs._tcp.domain.com
for more, read doc here (page 2) : https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/voice_ip_comm/jabber/10_6/CJAB_BK_C56DE1AB_00_cisco-jabber-106-deployment-and-installation-guide/CJAB_BK_C56DE1AB_00_cisco-jabber-106-deployment-and-installation-guide_chapter_01111.pdf
Service Profile Configuration
Imported Users
Cisco Unified Client Services Framework SIP
Presence Gateway Configuration
SSL Certificate Management: Cisco Unified CM and Cisco Unified IM and Presence
Our deployment provisioning is complete. Clients should now be able to launch and use Cisco Jabber. However, one final deployment task remains and that is SSL Certificate Management.
Currently both the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (cucm.ad.crs) and the Cisco Unified IM and Presence Server (cups.ad.crs) are using self-signed SSL certificates generated during the installation process. Cisco Jabber relies on SSL certificate validation to establish secure connections with applications and services hosted on servers. In so doing, Cisco Jabber is authenticating the identity of the hosts to which it connects. Cisco Jabber will NOT automatically accept any certificate issued by an untrusted Certificate Authority (CA), and this includes self-signed certificates.
In order to establish an environment for secure connectivity we MUST deploy CA signed certificates across all Cisco Collaboration applications in the environment. This is also a requirement for implementation of Mobile and Remote Access with Cisco Expressway, and SAML Single Sign-On; both addressed later in the lab.
Establish Root CA Trust
Download CA Root Certificate from CA server
Upload the CA Root Certificate to Unified CM
Tomcat Trust
Tomcat
Request and Install a CA Signed Tomcat Certificate
Set the following values in the Certificate Signing Request dialog:
• Certificate Purpose: tomcat
• Distribution: Multi-Server(San)
• Key Length: 2048
• Hash Algorithm: SHA256
Click Download CSR from the menu.
Choose Notepad from the list. Click OK.
From the Notepad main menu choose Format > Word Wrap.
Request a Certificate
Upload the CA Root Certificate to Unified IM and Presence
Request and Install a CA Signed XMPP-Trust Certificate
Service Maintenance to Finalize Certificate Installation
Restart Cisco Tomcat for the Unified CM Cluster
utils service restart Cisco Tomcat
Restart Cisco Tomcat for the Unified IMP
utils service restart Cisco Tomcat
utils service restart Cisco XCP Router
Deactivate and Activate the Cisco Tftp Service on UCM
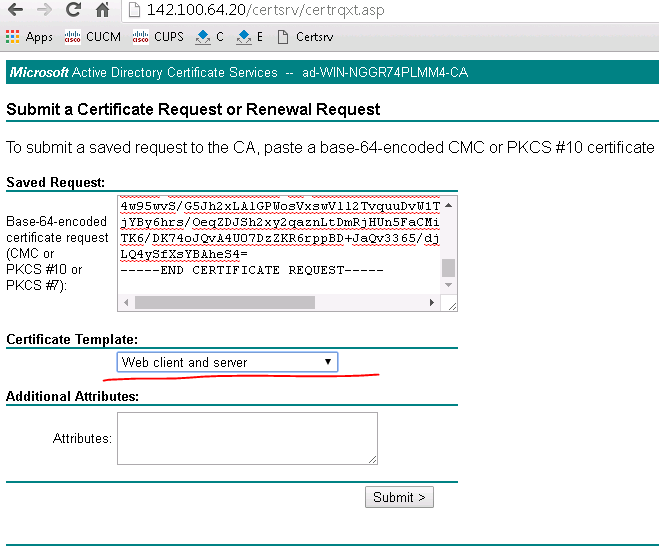
Enable AD CS to Issue “Client and Server” Certificate
The default ‘web server’ certificate template in AD CS creates a certificate for Server Authentication. The server certificate for the Expressway also needs Client Authentication if you want to configure a neighbor or traversal zone with mutual authentication (where TLS verify mode is enabled)
Configure Expressway-E for Unified Communications
Certificate Management for Expressway
CA
Server certificate
Expe
Expc
Download CSR
Restart both
Configure Expressway-C for Unified Communications
Configure Unified Communications Domains
You must identify the domains for which registration, call control, provisioning, messaging, and presence services are to be routed to Unified CM.
Discovering IM and Presence Services
Discovering Unified CM Services
Create a Secure Traversal between Expressway-E and Expressway-C
Zone Status
Upload Jabber Configuration file
<config version="1.0">
<Policies>
<EnableSIPURIDialling>true</EnableSIPURIDialling>
<VoiceServicesDomain>YOURDOMAIN</VoiceServicesDomain>
</Policies>
<Directory>
<SipUri>mail</SipUri>
<UseSIPURIToResolveContacts>true</UseSIPURIToResolveContacts>
<BDISipUri>mail</BDISipUri>
<BDIUseSIPURIToResolveContacts>true</BDIUseSIPURIToResolveContacts>
<BusinessPhone>ipphone</BusinessPhone>
<UDSPhotoURIWithToken>http://server/%%uid%%.jpg</UDSPhotoURIWithToken>
</Directory>
</config>
Restart CUCM TFTP service
No comments:
Post a Comment